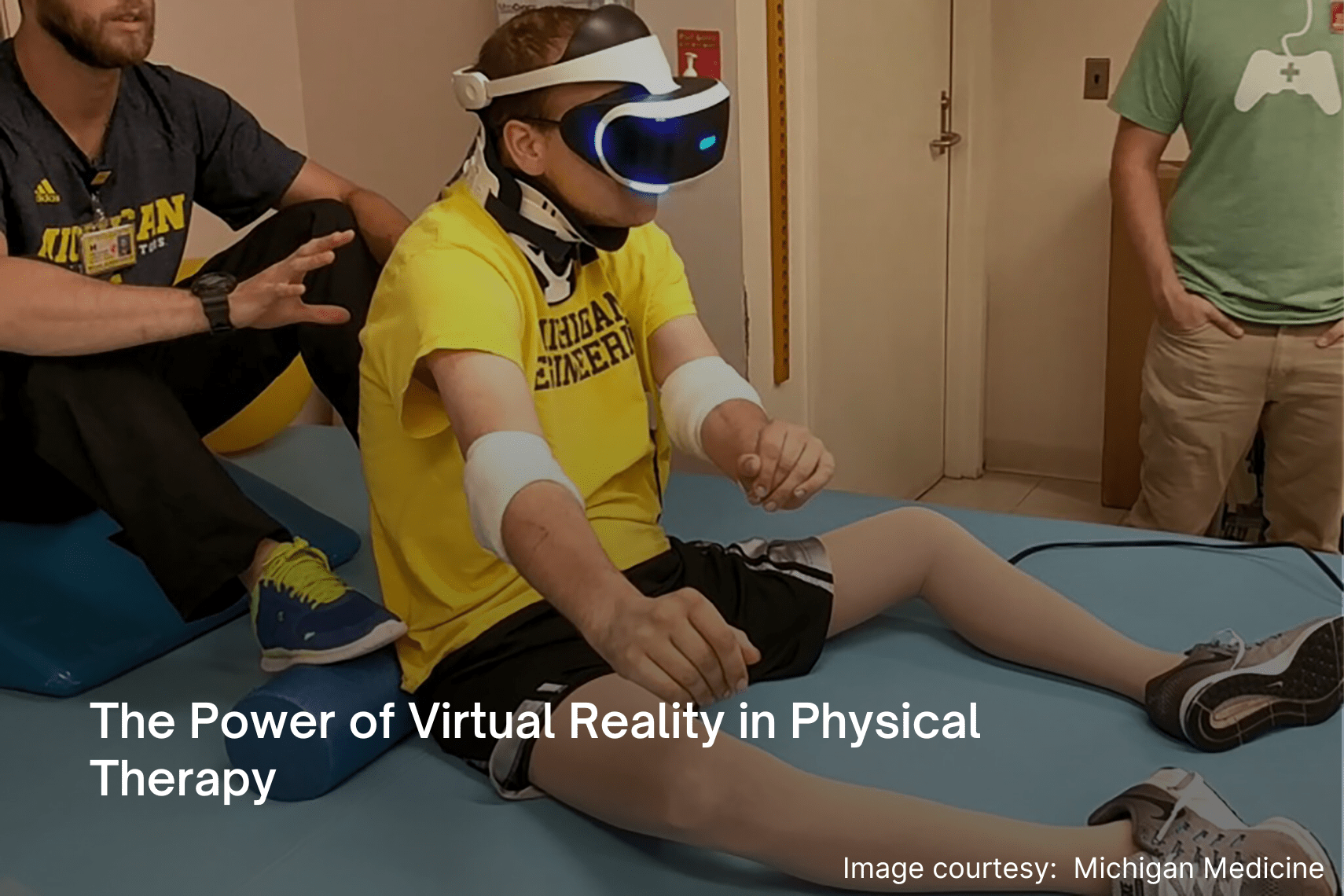
As a physical therapist, I have witnessed firsthand how the field of physical therapy is constantly evolving and am always on the lookout for new and innovative ways to treat patients and educate them. Every day, new modalities and techniques emerge that can help us better serve our patients and improve their outcomes. One such modality that has been gaining traction in recent years is therapeutic virtual reality (TVR). With its ability to create immersive digital environments that simulate real-world scenarios, TVR has the potential to revolutionize the way we treat a variety of conditions. VR technology creates an immersive digital environment that allows patients to experience real-world scenarios in a safe and controlled environment. Therapeutic virtual reality has been shown to improve outcomes in physical therapy and has been used to treat a variety of conditions.
One area where TVR has shown particular promise is in vestibular rehabilitation. Vestibular rehabilitation is a specialized form of therapy intended to alleviate both the primary and secondary problems due to vestibular disorders. It is an exercise-based program primarily designed to reduce vertigo and dizziness, reduce gaze instability, and/or reduce imbalance and fall risk as well as address any secondary impairments that are a consequence of the vestibular disorder. Patients with vestibular disorders often experience symptoms such as dizziness, vertigo, and imbalance. These symptoms can be debilitating and can significantly impact a patient’s quality of life. TVR can be used to simulate different visual and vestibular stimuli, allowing patients to gradually adapt to the stimuli and reduce the intensity of their symptoms. Studies have shown that TVR can be an effective tool for reducing vertigo and improving balance and gait in patients with vestibular disorders.
TVR also has the potential to be used in the treatment of neurological conditions such as stroke, spinal cord injury, and Parkinson’s disease. One of the key benefits of TVR is its ability to create immersive environments that simulate real-world scenarios. This can be especially helpful in the treatment of neurological conditions, where patients often need to relearn how to perform everyday tasks. TVR can be used to simulate these tasks in a safe and controlled environment, allowing patients to practice and improve their skills without the risk of injury.
In the treatment of stroke, TVR can be used to improve upper extremity function. Studies have shown that TVR can be an effective tool for promoting motor recovery and improving functional outcomes in stroke patients. Similarly, in the treatment of spinal cord injury, TVR can be used to improve motor function and promote neural plasticity. By simulating different movements and activities, TVR can help patients develop new neural pathways and regain function.
In the treatment of Parkinson’s disease, TVR can be used to improve balance and gait. Patients with Parkinson’s disease often experience problems with balance and gait, which can increase their risk of falls and limit their mobility. TVR can be used to simulate different scenarios and environments, allowing patients to practice and improve their balance and gait in a safe and controlled environment. Studies have shown that TVR can be an effective tool for improving balance and gait in patients with Parkinson’s disease.
TVR can also be used to help athletes recover from injuries and prevent future injuries. In the treatment of sports injuries, TVR can be used to improve proprioception and balance. By simulating different playing environments and conditions, TVR can help athletes develop their balance and stability. Additionally, TVR can be used to assess an athlete’s biomechanics and identify areas of weakness or potential injury. This information can then be used to develop individualized training programs that target specific areas of need.
Injury prevention is another area where TVR can be a valuable tool. By simulating different scenarios and environments, TVR can help athletes develop their decision-making skills and improve their ability to anticipate and avoid potential injuries. Additionally, TVR can be used to assess an athlete’s biomechanics and identify areas of weakness or potential injury. This information can then be used to develop training programs that target specific areas of need and reduce the risk of injury.
Therapeutic virtual reality is a versatile tool that can be used to treat a wide range of conditions in the field of physical therapy. Its ability to create immersive environments that simulate real-world scenarios makes it a valuable tool in the treatment of vestibular disorders, neurological conditions, and sports injuries. As physical therapists, it is our responsibility to stay up-to-date with the latest technologies and treatment modalities, and TVR. That being said, virtual reality is still an emerging form of therapy. While VR has shown great potential, it may not be feasible for everyone at this time. Some patients may not have access to the necessary equipment or may not be able to tolerate the virtual environment due to nausea or other side effects. Additionally, the field of therapeutic VR is still in its early stages and further research is needed to fully understand its effectiveness and limitations.
However, as technology continues to evolve and become more accessible, the potential benefits of VR in physical therapy will likely continue to expand. As physical therapists, we must continue to stay informed and open-minded about new modalities and treatments that can improve the lives of our patients. By combining our expertise with the latest technologies, we can help our patients achieve optimal outcomes and live their best lives.
